Transpalpebral tonometer application during intraocular pressure evaluation in the patients with refraction anomaly before and after keratophotorefractive surgery
Great success of the modern keratorefractive surgery, especially excimerlaser cornea microsurgery (FRК, LASIK, LASEK, Epi-LASIK) and its wide spread require high attention to the eye morphophysiological rates in pre- and postoperational period. The most important rates are still the characteristics of the cornea, such as thickness and its changes, regenerative response of corneal tissue and its regulation, as well as the data of intraocular pressure (IOP) and their correlation with cornea metrical rates.
According to the data of numerous investigations, underestimation of IOP level during applanation tonometry in patients, which were subject to keratophotorefractive surgeries, is of great importance in glaucoma diagnostic search. Hence, the advantages of scleral tonometry application in this category of patients for ophthalmotone appropriate evaluation and timely ophthalmohypertension detection are clear.
Purpose
The purpose of the study is to evaluate the clinical use of transpalpebral scleral tonometry, reliability of its application in the patients with refraction anomaly in pre- and postoperational period, dynamics of eye morphometric rates (pachymetry of the central corneal zone, IOP) and their correlative bond before and after photorefractive surgeries.
Methods
We have analyzed the results of prospective comparative case series clinical study in 98 patients (194 eyes) with ametropia of various degrees, among which 59 persons (118 eyes) form the group of patients, who have no keratophotorefractive surgeries in past history, and 39 patients (76 eyes), which were the subject to excimerlaser vision correction (Epi-LASIK, LASIK, FRK) with various length of postoperational period from 7 days to 4 years.
The patients age distribution was from 18 to 53 years, the women make 61%, the men - 39%.
The following factors were exclusion criteria from the study:
Cornea pathology, influencing prognosticly the applanation tonometry results;
Upper eyelid and sclera pathology, which are the contraindications for transpalpebral diaton-tonometry.
Before and after the surgery all patients were subject to the complete refractive examination, including keratotopography and wavefront-aberrometry (AMO, USA). In a number of patients for cornea state morphologic evaluation we conducted US-biomicroscopy of the corneal optical zone before and in two months after laser correction (Picture 1).
Before and after surgery we trice measured pachymetry corneal thickness in central (4 points) zone - central corneal thickness (CCT) in each patient. We realized the study using two devices: US-pachymeter UP 1000 by NIDEK (Japan) and А-scan-pachymeter P55 by Paradigm (USA). IOP was measured with Goldmann applanation tonometer (Rodenstok, Germany), pneumotonometer (NIDEK, Japan) and transpalpebral scleral diaton tonometer (RSIME, Russia, picture 2) using traditional methodology (picture 3), all ophthalmotone measurements were realized the patients being in the sitting position with time interval being 2-3 minutes between two investigators.
The surgeries were carried out using excimer laser VISX Star S4 IR (AMO, USA), microkeratome LSK Evolution II (Moria, France) and epikeratome Centurion SES (Norwood, Australia)
Statistical treatment of the received results was realized using common methods of medical mathematical statistics. Statistic calculations were carried out using "Analysis Tools Pack". Determination of differences reliability between the groups being compared in the presence of normal distribution in sampling of one-type factors was realized using two-sample t-tests. Correlation analysis by Pearson allowed detecting the character of correlations between showings. Correlation with Р<0,05 was considered to be reliable.
Results and discussion
In 93,6% cases visual acuity without correction after surgery was 0,6 - 1,0 (Table 1) in the early postoperative period.
Results of the study are shown in Tables 2 and 3.
While analyzing morphometric parameters in the group of patients which were not the subject to photorefractive surgeries the mean PCT value was 554,5±32,4 m, and the mean value of applanational IOP - 16,1±2,6 mm Hg, the fluctuation being from 10 to 21 mm Hg; mean ophthalmotone level evaluated with diaton tonometer - 14,7±2,5 mmHg, the fluctuation being from 9 to 20 mmHg. At that correlation between values of the applanation tonometer and transpalpebral scleral diaton tonometer was highly reliable (r = 0,73, р±0,005). To define the advantages of scleral tonometry in comparison with the traditional keratoapplanational method we made calculations of real ophthalmotone in the patients of this group taking into account pachymetry (PCT), ophthalmometry and applanation tonometry data. Mean value of the real IOP after applanation value converting was 15,4±2,4 mmHg. Pearson correlation coefficient between real IOP (modified result, received with applanation tonometry) and the value, determined with diaton tonometer was 0,89, р<0,005, which shows high reliability of transpalpebral scleral tonometry.
In the groups of patients, underwent photorefractive vision correction, mean PCT was 499,8±50,9 m (fluctuations from 407 to 513 m), mean applanation value of IOP - 12,4±2,91 mmHg (fluctuations from 7 to 20 mm Hg), modified taking into account keratometry IOP rates - 13,9±3,0 mm Hg, mean diaton-tonometry result - 15,1±2,75 mm Hg. At that we notice approximation of diaton-tonometry figures to the modified applanation IOP value taking into consideration keratometric rates - increase of correlation coefficient from 0,51 to 0,81 (table 4).
Correlation analysis of PCT and IOP results in the group of patients, examined both in preoperational period and after photorefractive vision correction showed reliability of this correlation, p<0,005, reduction of IOP for 1 mm Hg is registered PCT being decreased for 29,7 m. At that difference between pre- and postoperational IOP during applanation tonometry was 3,5 mm Hg, and during diaton-tonometry - 1,8 mm Hg, that is statistically dissimilar (t>2, p<0,005), which shows significant advantage of ophthalmotone evaluation if we omit cornea.
Conclusion. Thus, cornea thickness is the important factor of IOP evaluation and monitoring and requires the necessity of including corneal pachymetry in the program of examination the patients with suspicion of glaucoma and hypertension, especially after various keratorefractive surgeries while using the traditional corneal methods of ophthalmotonometry. At the same time clinical application of transpalpebral scleral diaton tonometer makes it possible to evaluate IOP using only one device, the procedure being efficient, economical, simple in performance and requiring no additional instrumental examination.
Literature
Nesterov A.P. Transpalpebral tonometer for intraocular pressure measuring.// Ophthalmology Bulletin - 2003. - Vol. 119. - №1. - P. 3 - 5.
Blaker JW, Hersh PS. Theoretical and clinical effect of preoperative corneal curvature on excimer laser photorefractive keratectomy for myopia.//Refract. Corneal Surg. - 1994;-Vol.10:P. 571-574.
Buratto L, Ferrari M, Genisi C. Myopic keratomileuesis with the excimer laser: one-year follow-up.//Refract. Corneal Surg. - 1993;-Vol.9:P.12-19.
Cennamo G, Rosa N, La Rana A, et al. Non-contact tonometry in patients that underwent photorefractive keratectomy.//Ophthalmologica.- 1997;-Vol. 211:P.341-343
Duch S, Serra A, Castanera J. Tonometriy after laser in Situ keratomileusis treatment. //J Glaucoma. - 2001. - Vol.10. - P. 261 - 265.
Emara B.et al. Correlation of intraocular pressure and corneal thickness in normal myopic eyes and after laser in situ keratomileusis.//J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. - 1998;-Vol.24(10):P. 1320-1325
Mardelli PG, Piebenga LW, Whitacre MM. The effect of excimer laser photorefractive keratectomy on intraocular pressure measurements using the Goldmann applanation tonometer //Ophthalmol. - 1997. - Vol.104. - P. 945-948.
Pandav SS, Ashok Sharma, Amit Gupta. Reliability of Proton and Goldmann applanation tonometers in normal and postkeratoplasty eyes. //Ophthalmol. - 2002. - Vol. 109. - P. 979-984.
Simon G, Small RH, Ren Q, et al. Effect of corneal hydration on Goldmann applanation tonometry and corneal topography.//Refract. Corneal Surg.- 1993;-Vol. 9:P.110-117
Vakili R, Choudhri SA, Tauber S, Shields MB. Effect of mild to moderate myopic correction by laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis on intraocular pressure measurements with goldmann applanation tonometer, tono-pen, and pneumatonometer. //J Glaucoma. - 2002. - Vol.11. - N6. - P. 493-496.
Whitacre MM, Stein R. Sources of error with use of Goldmann-type tonometers. //Surv Ophthalmol. - 1993. - Vol. 38. - P.1 - 30.
Wu X, Liu S, Huang P, Wang P. Analysis of intraocular pressure after myopic photorefractive keratectomy. //Chung Hua Yen Ko Tsa Chih. - 2002. - Vol.38. - N10. - P.603-605.
Zadok D, Raifkup F, Landao D. Intraocular pressure after LASIK for hyperopia. //Ophthalmol. - 2002. - Vol. 109. - P.1659-1661.
Picture 1 Topographic ultrasonic biomicroscopy of the cornea in optical zone of normal myopia eye (А), after PRK (B) and after LASIK (C)
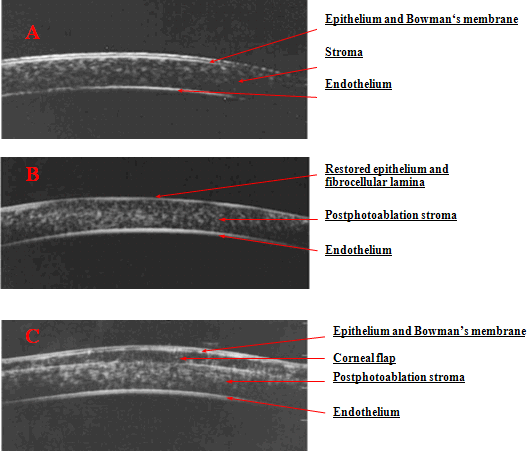 Cornea, as the basic optical lens of the eye, is the main element to be influenced during various, and first of all laser, surgeries with refractive, reconstructive, optical and other purposes. Picture 2 Transpalpebral scleral diaton tonometer
Cornea, as the basic optical lens of the eye, is the main element to be influenced during various, and first of all laser, surgeries with refractive, reconstructive, optical and other purposes. Picture 2 Transpalpebral scleral diaton tonometer
Picture 3 Methodology of transpalpebral tonometry
Table 1 Visual activity dynamics in patients after keratophotorefractive vision correction Visual activity Age of the patients with ametropia
| Visual activity | Age of the patients with ametropia | ||||
| before 25 | 26-35 | 36-45 | 46 and older | total | |
| UCVA before surgery | 0.096 | 0.0106 | 0.097 | 0.067 | 0.098 |
| UCVA after surgery | 0.945 | 0.87 | 0.836 | 0.767 | 0.889 |
Table 2 Morphometric description of the group of patients with refraction anomaly, which were not subject to surgical laser vision correction Morphometric indexes
|
Morphometricindexes |
M±SD |
min |
max |
|
|
Ophthalmotonometry |
43,8±1,4 |
36,5 |
46,75 |
|
|
Pachymetry central corneal thickness |
554±32,4 |
471 |
637 |
|
|
Applanation tonometry |
16,1±2,6 |
10 |
21 |
R (р<0,005)
0,73 |
|
Transpalpebral diaton tonometry |
14,7±2,5 |
9 |
20 |
Table 3 Morphometric description of the group of patients after keratophotorefractive ametropia correctionMorphometric indexes
|
Morphometricindexes |
M±SD |
min |
max |
|
|
Ophthalmotonometry |
39,8±2,48 |
34,5 |
46,5 |
|
|
Pachymetry central corneal thickness |
499±50,9 |
399 |
610 |
|
|
Applanation tonometry |
12,4±2,91 |
7 |
20 |
R (р<0,05)
0,51 |
|
Transpalpebral diaton tonometry |
15,1±2,75 |
10 |
21 |
Table 4 Correlation analysis of opthalmotonometry rates in patients before and after photorefractive surgeriesOphthalmotonometry results Correlation coefficient
|
Ophthalmotonometry results |
Correlation coefficient r, p<0,005 |
|
|
Preoperationalperiod |
Postoperationalperiod |
|
|
Applanation corneal/ Transpalpebral scleral tonometry |
0,73 |
0,51 |
|
Modified applanation corneal/ Transpalpebral scleral tonometry |
0,89 |
0,81 |